
Yellowstone Lake
Yellowstone Lake is a significant freshwater resource located in Teton County, Wyoming, with an area of 87,046 acres. Situated at an elevation of 7,733 feet (2,357 m) above sea level, it is the largest high elevation lake in North America, and is renowned for its stunning natural beauty and diverse aquatic ecosystem. With a length of approximately 20 miles (32.2 km) and a width of 14 miles (22.5 km), Yellowstone Lake boasts a shoreline spanning 141 miles (227 km) and a surface area of 132 square miles (342 km2). The lake is frozen completely every winter, with ice thickness varying from a few inches to over two feet. It typically thaws in late May or early June. Despite its impressive size, the water in Yellowstone Lake remains cold year-round, with an average temperature of 41°F (5°C), making swimming unsafe due to the risk of hypothermia. Yellowstone Lake is home to a diverse range of fish species, including the largest population of wild cutthroat trout in North America. The presence of these Pacific Ocean fish in a lake that drains to the Atlantic puzzled experts for years. However, recent research suggests that the lake once drained to the Pacific Ocean via Outlet Canyon and the Snake River, allowing fish to swim across the Continental Divide at Two Ocean Pass. The introduction of the invasive species lake trout now poses a significant threat to the native cutthroat trout population. The lake's only outlet is the Yellowstone River, which flows northward from the lake at Fishing Bridge. The elevation of the lake's northern end remains relatively consistent until LeHardy Rapids, leading many to consider the rapids as the true northern boundary of the lake. In conclusion, Yellowstone Lake is a spectacular freshwater resource in Teton County, Wyoming, with an extensive area and diverse ecosystem. While it remains a popular destination for recreational activities such as fishing, boating, and wildlife viewing, visitors must exercise caution due to the extreme cold of the water. The lake's unique history and present-day challenges provide a fascinating glimpse into the complex interactions between geology, climate, and ecology in the region.
Read more
Yellowstone Lake
Yellowstone Lake is a significant freshwater resource located in Teton County, Wyoming, with an area of 87,046 acres. Situated at an elevation of 7,733 feet (2,357 m) above sea level, it is the largest high elevation lake in North America, and is renowned for its stunning natural beauty and diverse aquatic ecosystem. With a length of approximately 20 miles (32.2 km) and a width of 14 miles (22.5 km), Yellowstone Lake boasts a shoreline spanning 141 miles (227 km) and a surface area of 132 square miles (342 km2). The lake is frozen completely every winter, with ice thickness varying from a few inches to over two feet. It typically thaws in late May or early June. Despite its impressive size, the water in Yellowstone Lake remains cold year-round, with an average temperature of 41°F (5°C), making swimming unsafe due to the risk of hypothermia. Yellowstone Lake is home to a diverse range of fish species, including the largest population of wild cutthroat trout in North America. The presence of these Pacific Ocean fish in a lake that drains to the Atlantic puzzled experts for years. However, recent research suggests that the lake once drained to the Pacific Ocean via Outlet Canyon and the Snake River, allowing fish to swim across the Continental Divide at Two Ocean Pass. The introduction of the invasive species lake trout now poses a significant threat to the native cutthroat trout population. The lake's only outlet is the Yellowstone River, which flows northward from the lake at Fishing Bridge. The elevation of the lake's northern end remains relatively consistent until LeHardy Rapids, leading many to consider the rapids as the true northern boundary of the lake. In conclusion, Yellowstone Lake is a spectacular freshwater resource in Teton County, Wyoming, with an extensive area and diverse ecosystem. While it remains a popular destination for recreational activities such as fishing, boating, and wildlife viewing, visitors must exercise caution due to the extreme cold of the water. The lake's unique history and present-day challenges provide a fascinating glimpse into the complex interactions between geology, climate, and ecology in the region.
Read more detailsCurrent Conditions
Water Temperature
Current water temperature for Yellowstone Lake is 32°F.
Current Snapshot
Forecast: Wednesday, May 7
PartlyCloudy
Hourly Insights
Temperature
Precipitation
Wind
Sun, Moon & UV
Solunar Fishing Forecast
Todays action is rated a 2 (scale is 0 thru 5, 5 is the best)
6:00 AM - 6:00 AM
12:33 PM - 3:03 PM
9:24 PM - 10:54 PM
9:30 AM - 11:00 AM
Outlook for Wednesday at Yellowstone Lake
Expect temperatures ranging from 29°F to 52°F. Skies look partly cloudy with little chance of precipitation. Winds will be averaging 5 mph, with potential gusts reaching up to 15 mph. The maximum UV index will be 7 (High), so plan sun protection accordingly. For anglers, today's fishing action is rated 2/5 (Todays action is rated a 2 (scale is 0 thru 5, 5 is the best)). Look for the best bite times during the major periods around 6:00 AM and 12:33 PM, or try the minor windows near 9:24 PM and 9:30 AM for potential early morning or evening action. Check back for the latest conditions and forecasts for Yellowstone Lake.
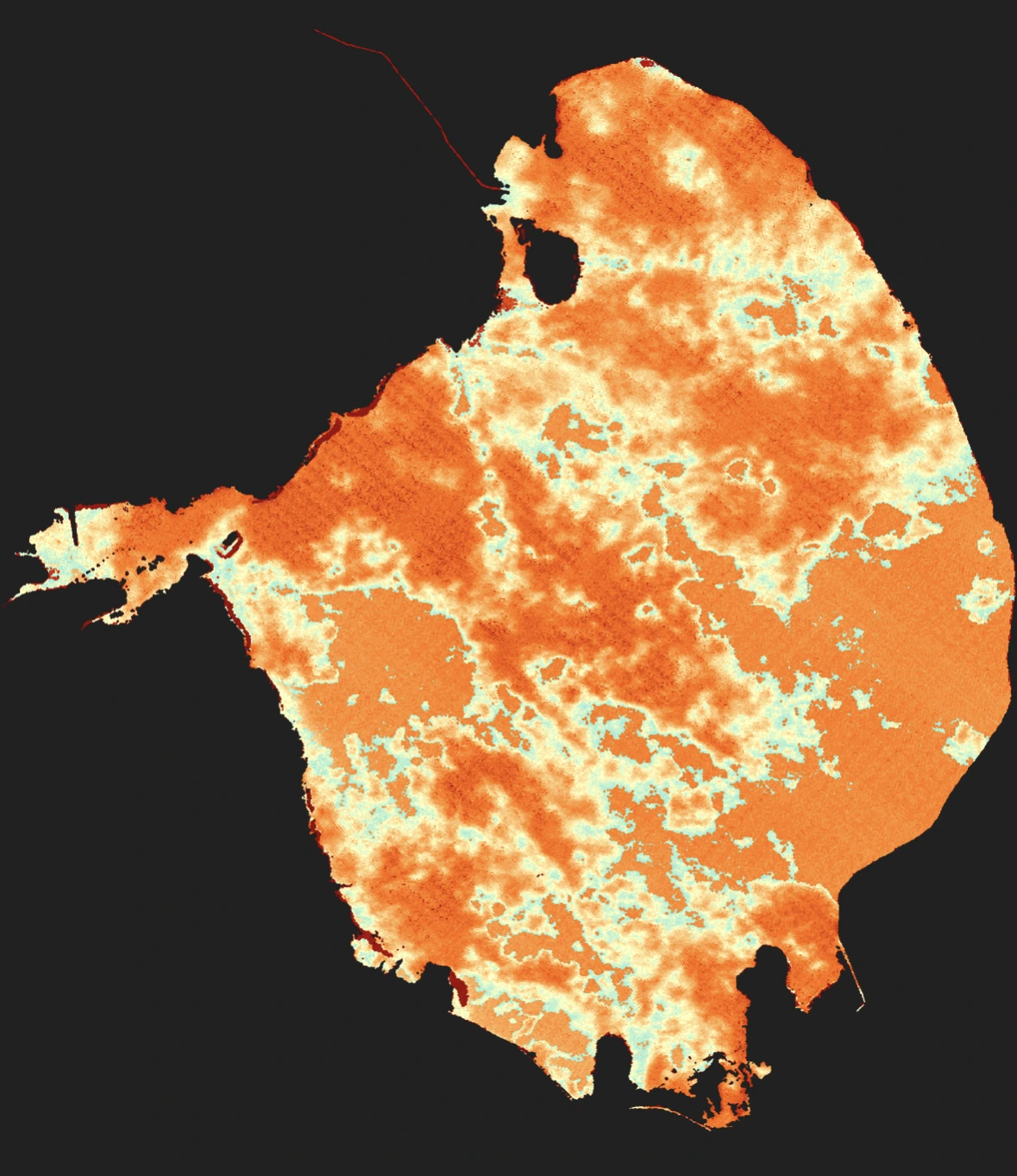
Lake Map Views

Try Premium Features
Find the fishing sweet spots! See detailed temperature readings throughout your lake.
No credit card required for preview
Lake Information
Common Fish Species
Nearby Lakes
Water Temperature History
Trends for Yellowstone Lake
Current Temp
Latest recorded surface temperature.
Lowest in Period
32°F
On Mar 16
Coldest point in the Last 12 Months.
Average in Period
42°F
Typical temp during the Last 12 Months.
Temperature Trend: Last 12 Months
Surface temperature over the selected period.
Key Observations (Last 12 Months)
- Warmest avg: July (59°F).
- Coolest avg: April (35°F).
- Rapid warming often occurs: June → July (+12°F).
- Sharpest cooling trend: September → October (-10°F).
Weather Forecast
Wind speed and pressure trends
Hourly Wind Forecast
Wind Direction
115°
Pressure
1021 mb
Cloud Cover
5%
Visibility
14 miles
Daily Pressure Forecast
Frequently Asked Questions About Yellowstone Lake
Get accurate, up-to-date information about conditions at Yellowstone Lake.